Function of Nucleus










Function of Nucleus
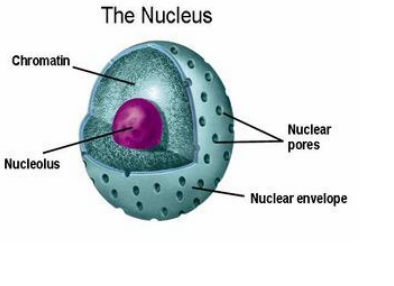
Nucleus
In Animal cells, nucleus lies at the centre of the cell whereas in Plant cells, it is present at the periphery of the cell due to presence of a large vacuole. The nucleus consists of the following four parts:
Functions of Nucleus:
________________ is genetic recombination takes place? | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Fluid present inside nucleus is specifically known as___________________. | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Which cell organelle is known as the control centre of the cell? | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [20]
It has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thWhen I have not joined Abhyas Academy, my skills of solving maths problems were not clear. But, after joining it, my skills have been developed and my concepts of science and SST are very well. I also came to know about other subjects such as vedic maths and reasoning.

Sharandeep Singh
7thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thThird consective year,my ward is in Abhyas with nice experience of admin and transport support.Educational standard of the institute recumbent at satisfactory level. One thing would live to bring in notice that last year study books was distributed after half of the session was over,though study ...

Ayan Ghosh
8thIn terms of methodology I want to say that institute provides expert guidence and results oriented monitering supplements by requsite study material along with regular tests which help the students to improve their education skills.The techniques of providing education helps the students to asses...

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thAbhyas institute is one of the best coaching institute in the vicinity of Ambala cantt.The institute provides good and quality education to the students.The teachers are well experienced and are very helpful in solving the problems. The major advantages of the institute is extra classes for weak...

Shreya Shrivastava
8thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very nice or it can be said wonderful. I have been studying here from seven class. I have been completing my journey of three years. I am tinking that I should join Abhyas Academy in tenth class as I am seeing much improvement in Maths and English

Hridey Preet
9thWe started with lot of hope that Abhyas will help in better understnding of complex topics of highers classes. we are not disappointed with the progress our child has made after attending Abhyas. Though need to mention that we expected a lot more. On a scale of 1-10, we would give may be 7.

Manya
8thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thAbhyas academy is great place to learn. I have learnt a lot here they have finished my fear of not answering.It has created a habit of self studying in me.The teachers here are very supportive and helpful. Earlier my maths and science was good but now it has been much better than before.

Barkha Arora
10thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thUsually we see institutes offering objective based learning which usually causes a lag behind in subjective examinations which is the pattern followed by schools. I think it is really a work of planning to make us students grab the advantages of modes of examination, Objective Subjective and Onli...

Anika Saxena
8thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.
